STRUGGLING With Stubborn Fat That Won’t Disappear? No Matter Your Age, No Matter What You Try...
It’s Still There…!
Absolutely Free Training Video
Reveals
The Game-Changing Secret To Vaporize Fat Cells!
Click the button below now, to Watch your Absolutely Free Training Video before it’s gone!
=> Yes ! Watch My Free Video Now !
Hello friends. Welcome to yet another useful article. Today we are going to learn about an imaging technique called Dexa Scan.
What is a DEXA scan?
A DEXA scan, or Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry scan, is a medical imaging technique specifically designed to assess bone density and other body compositions.
Primarily used to assess osteoporosis and fracture risk, this scan uses two different energy levels of X-rays to ascertain bone mineral content (calcium) and differentiate between lean muscle mass and fat mass in the body.
Its non-invasive nature makes it an attractive option for both patients and healthcare providers as it does not require needles or injections, allowing for a pleasant experience during the assessment.
The DEXA scan process is relatively simple. Patients lie flat on a scanning table while the machine passes over them, sending out a mixture of low-dose x-rays.
This technique not only provides accurate measurements of bone density, but also effectively calculates muscle and fat composition throughout the body.
During my own DEXA scan session, I observed the seamless operation of the machine and the accuracy with which it analyzed my body composition, producing results that helped me make health decisions.”
Doctors often recommend DEXA scans based on several factors, including age, gender, and medical history. For example, postmenopausal women and older adults are often recommended to have this scan because of their increased risk of developing osteoporosis.
In addition, the results of a DEXA scan can serve as a starting point for monitoring changes in bone density over time, especially for those receiving treatment or lifestyle changes aimed at improving bone health.
In short, the DEXA scan is a valuable tool for assessing body composition, highlighting its central role in monitoring bone health, muscle mass and body fat.
Thanks to its advanced technology and non-invasive approach, it continues to gain recognition in both clinical and research settings for its reliability and accuracy.
Let’s learn about this useful imaging technique today…
Indications for a DEXA scan
There are several indications for this important diagnostic tool that can significantly influence an individual’s health management and preventive treatment strategy.
A number of factors, including age, gender, family history, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices may lead your doctor to recommend a DEXA scan.
People over the age of 50 are often advised to have periodic DEXA scans because of the increased risk of osteoporosis and related age-related fractures.
Research shows that postmenopausal women are particularly susceptible to bone loss, which requires early screening to detect potential problems before they progress.
In men, although the risk is generally lower, those with conditions that can affect hormone levels or bone health, such as low testosterone, may also benefit from a DEXA scan.
Family history also plays a significant role; patients with a family history of osteoporosis or other similar conditions may be advised to schedule a DEXA scan even if they have no symptoms.
Likewise, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or long-term corticosteroid therapy, are at increased risk of bone loss and should consider regular evaluations with DEXA scans.”
Lifestyle choices can also influence the decision to start a DEXA scan.
Factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and sedentary lifestyles can all contribute to poor bone health, which is why healthcare providers recommend a DEXA scan to monitor a patient’s condition.
By identifying at-risk individuals through these various indications, healthcare professionals can take timely action to promote long-term health and well-being.
What does a dexa scan show?
Interpreting the results of a DEXA scan or Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry scan requires understanding measurements of bone density, muscle mass, and body fat percentage.
These scans produce comprehensive reports that can guide health care providers in assessing a patient’s health, particularly with respect to osteoporosis and body composition.
The primary focus of a DEXA scan is to measure bone mineral density (BMD), which is assessed against established reference values to determine the risk of fracture and bone disease.
Typically, bone density results are presented as T-scores and Z-scores.
The T-score compares an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult. A score of -1.0 or higher is considered normal, +/-1.0 to -2.5 indicates low bone density (osteopenia), and -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis.
Z-scores compare a patient’s bone density to that of peers, which can be especially valuable in diagnosing bone health in younger populations.
In addition to bone density, the DEXA scan evaluates body composition by measuring fat mass and lean mass. The results tell you the percentage of body fat, which is crucial in determining general health risks.
Adult body fat percentages, which are typically considered healthy, range between 10-20% for men and 18-28% for women. Values outside these limits may indicate obesity or underweight, which may require further testing or lifestyle changes.
Healthcare professionals interpret these findings in conjunction with patient history and other diagnostic tests. Age, gender, and ethnicity affect these values, and thus the reference ranges are adjusted accordingly to obtain personal health assessments.
This nuanced approach ensures that individuals receive tailored recommendations aimed at improving or maintaining bone health and overall body composition.
Preparing for a dexa scan
If your doctor has ordered you to have a Dexa scan, you must follow these instructions:
- Avoid eating or drinking anything except water for at least 4 hours before the scan.
- Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, suspect you may be pregnant, or have a history of allergies to contrast agents.
- Remove all jewelry, glasses, and other objects that may interfere with the scan.
- Discuss the medications you are taking with your healthcare provider, as some medications may be necessary.
- Arrive on time to fill out the necessary paperwork and relax before the scan.
Steps of a Dexa scan
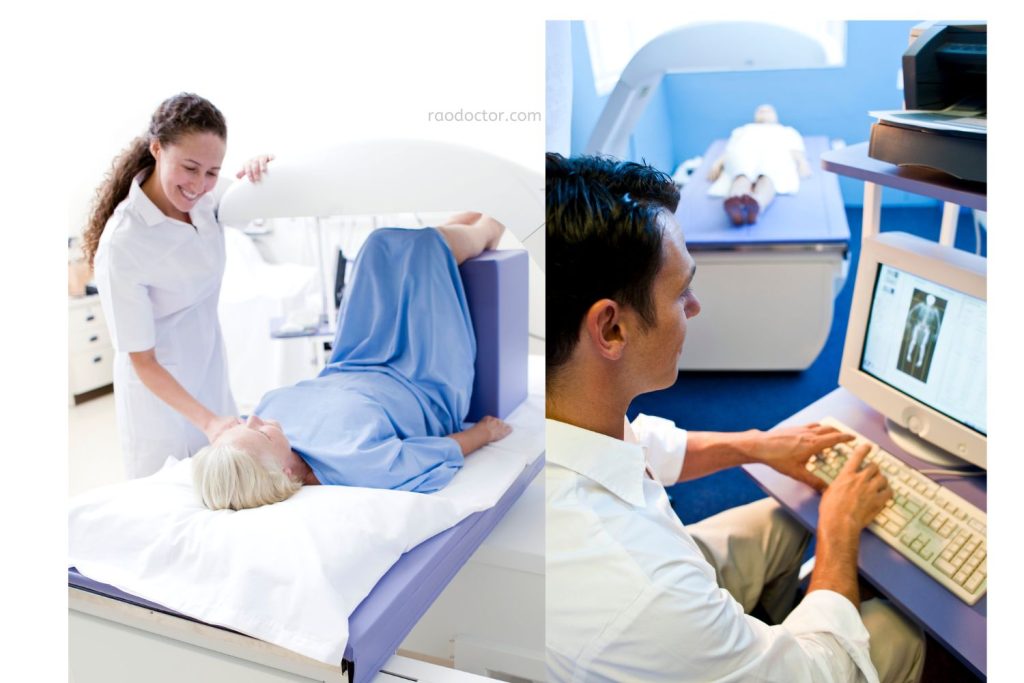
- Lie on the scanning table, usually on your back [as shown above]. The technician will line up your body with the scanner.
- Stay still during the scan, which usually takes about 10-30 minutes.
- The machine takes pictures of your bones, often focusing on the pelvis and spine.
- After the scan, you can get dressed and resume normal activities.
- The results will be analyzed and shared with you at a follow-up visit.
How to read a dexa bone density scan?
Bone mineral density results are important indicators of an individual’s bone health, typically obtained from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA).
This non-invasive imaging technique measures mineral density in bones and provides a detailed analysis using two key parameters: T-scores and Z-scores. [see the image below].

Understanding these points can help assess fracture risk and overall bone health.
The T-score compares an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult, which serves as a crucial benchmark.
A T-score of -1.0 or higher indicates normal bone density, while values between -1.0 and -2.5 indicate low bone density, known as osteopenia.
A T-score of -2.5 or less classifies a person as having osteoporosis, which significantly increases the risk of fracture.
Therefore, higher T-scores reflect better bone health, while lower scores indicate the need for interventions to prevent complications.
On the other hand, the Z-score evaluates bone density in relation to a person’s age, gender and ethnicity. This score helps identify whether bone density is appropriate for an individual’s body composition profile.
A Z-score below -2.0 is often considered below average and may require further investigation to rule out underlying health problems affecting bone density, especially in younger individuals. In contrast, Z-scores between -2.0 and +2.0 are typically considered normal.
Thus, both T-scores and Z-scores obtained from a DEXA scan play a significant role in understanding bone health.
Why and when does your doctor suggest a Dexa scan?
The dexa scan points mentioned above can help your doctor determine if you have bone health issues [e.g. osteoporosis] or body fat [obesity] and muscle mass problems such as sarcopenia.
Tracking your progress is like keeping score in a game. it guides your strategy to improve performance and make smart choices to strengthen your defenses against potential setbacks such as osteoporosis and sarcopenia, as well as improve bone strength and reduce the risk of fractures. .
Helpful resource – DXA Body Composition Analysis
We’ll stop here and learn more about this useful imaging technique in my next article.
In the meantime, if you find this article useful, please share it with your friends using the social media icons at the bottom of this article or Click to tweet below –
Dexa Scan – What it is and its uses Share on X
Bye. See you in my next article. This is now published. You can access it by clicking here – Dexa Scan benefits.
To get my latest articles delivered to your inbox, join my email list below:
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to submit the form